Inference
The Inference functionality empowers users to effortlessly generate multi-model schemas from existing single-model datasets. By utilizing compose schema inference techniques and schema editing operations, complex datasets can be transformed into well-structured multi-model representations. Enabling the generation of generally usable multi-model data.
The integration of the inference functionality was achieved by incorporating MM-infer1—a tool previously developed by our research team members—as a dedicated module within the system. This module leverages MM-infer’s schema inference capabilities, enabling the automatic generation of schema representations from single-model datasets.
A key component of this integration is the creation of a new Schema Conversion Component. This component is responsible for converting the output of MM-infer, the Record Schema Description (RSD)1, into the Schema Category format, while also managing the creation of Mapping.
Furthermore, the integration was enhanced by Inference Editor which enables real live editing of the inferred Schema Category.
And finally, the addition of the inference functionality showed the need for an improved version of the Mapping Editor.
Through this integration, users are now able to infer and adjust a Schema Category from any input data stored in a single-model format.
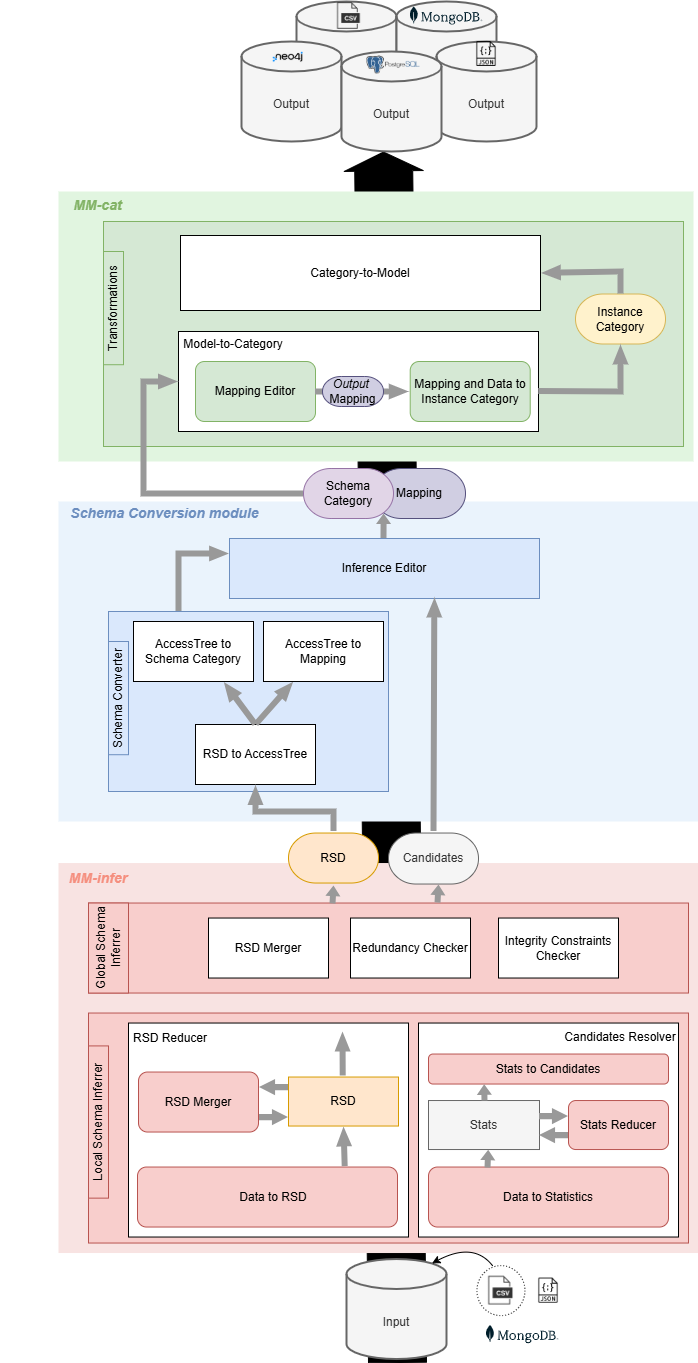
The overall architecture of the integrated tools as well as the data flow during multi-model data generation is depicted on the picture below.
It consists of three main modules with the flow beginning at the Input Layer, where data, such as raw files or data stored in database systems is ingested into the system.
In the MM-infer Module, the system applies a two-tier schema inference approach. First, the Local Schema Inferer analyzes the raw input data to generate raw schema descriptions (RSDs). These RSDs are then reduced and processed to produce statistical data and candidate properties, which are further refined in the Global Schema Inferer. At this stage, redundant information is removed, and integrity constraints are validated. The resulting consolidated RSDs and candidate properties are prepared for the next stage of the process.
The data then flows into the Schema Conversion Module. This module converts the raw schema descriptions into a more structured and intermediate representation called AccessTree. The Schema Converter transforms these AccessTrees into schema categories and mappings, which define how the input data can be interpreted and organized. The Inference Editor provides tools to refine these schema categories and mappings.
Once the schema categories and mappings are finalized, the data transitions to the MM-cat Module. This module is responsible for transforming the refined schema categories and mappings into models suitable for specific outputs. The Mapping Editor enables users to create or adjust mappings that translate schema categories into output formats or database models. These mappings can then be applied to generate Instance Categories, which represent structured data ready for storage or further use. The MM-cat module supports exporting the data into various outputs.
This modular architecture ensures a streamlined and efficient process, from raw data ingestion to multi-model outputs. Each module contributes a distinct functionality, while their integration creates a cohesive system capable of handling complex multi-model data generation tasks.
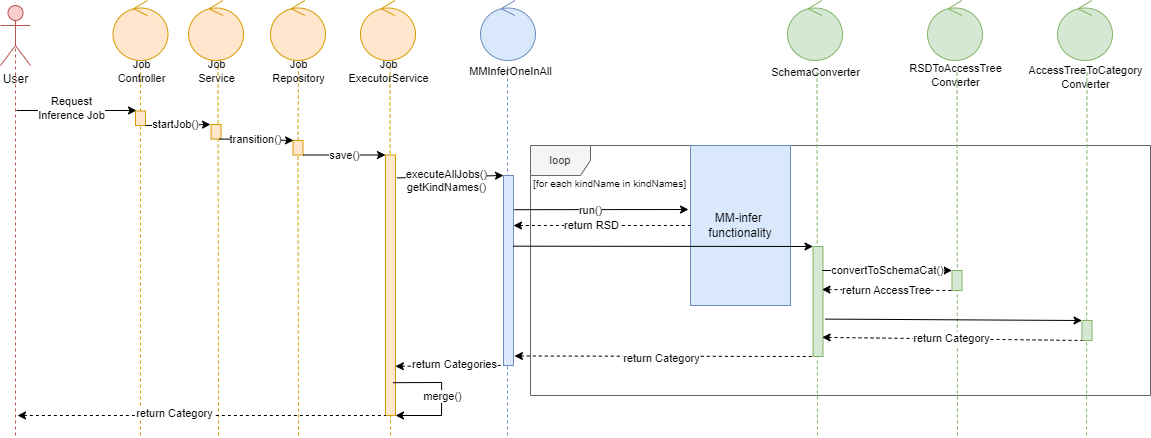
Detailed class design and structure of MM-infer is documented separately in the tool’s documentation, here we present the underlying classes that make up the Schema Conversion Component and the Inference Editor.
Acts as a wrapper for handling the conversion of the Record Schema Description (RSD) into the Schema Category and Mapping. It serves as an intermediary class whose main responsibility is to encapsulate the RSD as its input and apply the conversion logic via the convertToSchemaCategoryAndMapping(). Upon receiving the RSD, this method applies a series of transformations secured by the following classes.
Takes the input RSD structure, traverses it and creates an instance of a tree object called AccessTreeNode, whose nodes encompass all the necessary information for further steps.
Traverses the tree structure and converts it into a Schema Category.
Last, but not least, the information collected in the tree is also used for the creation of Mapping.
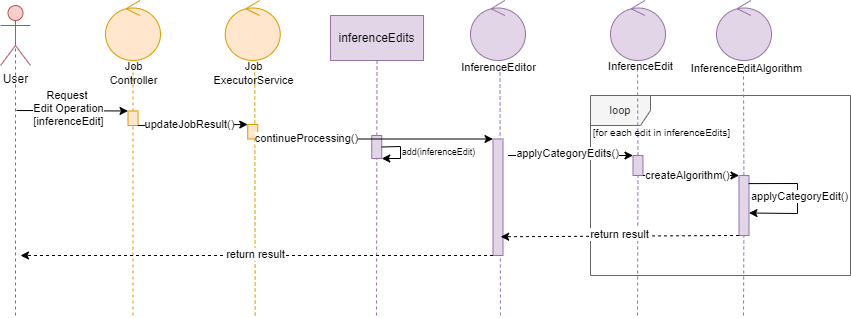
If the inferred Schema Category is too complex and unreadable, the Inference Editor comes into play. The available edit operations are encompassed by these classes.
The wrapper class for inferred Schema Category editing. Created with a list of instances of the InferenceEdit from which it creates the InferenceEditAlgorithm instances and applies the editing operations.
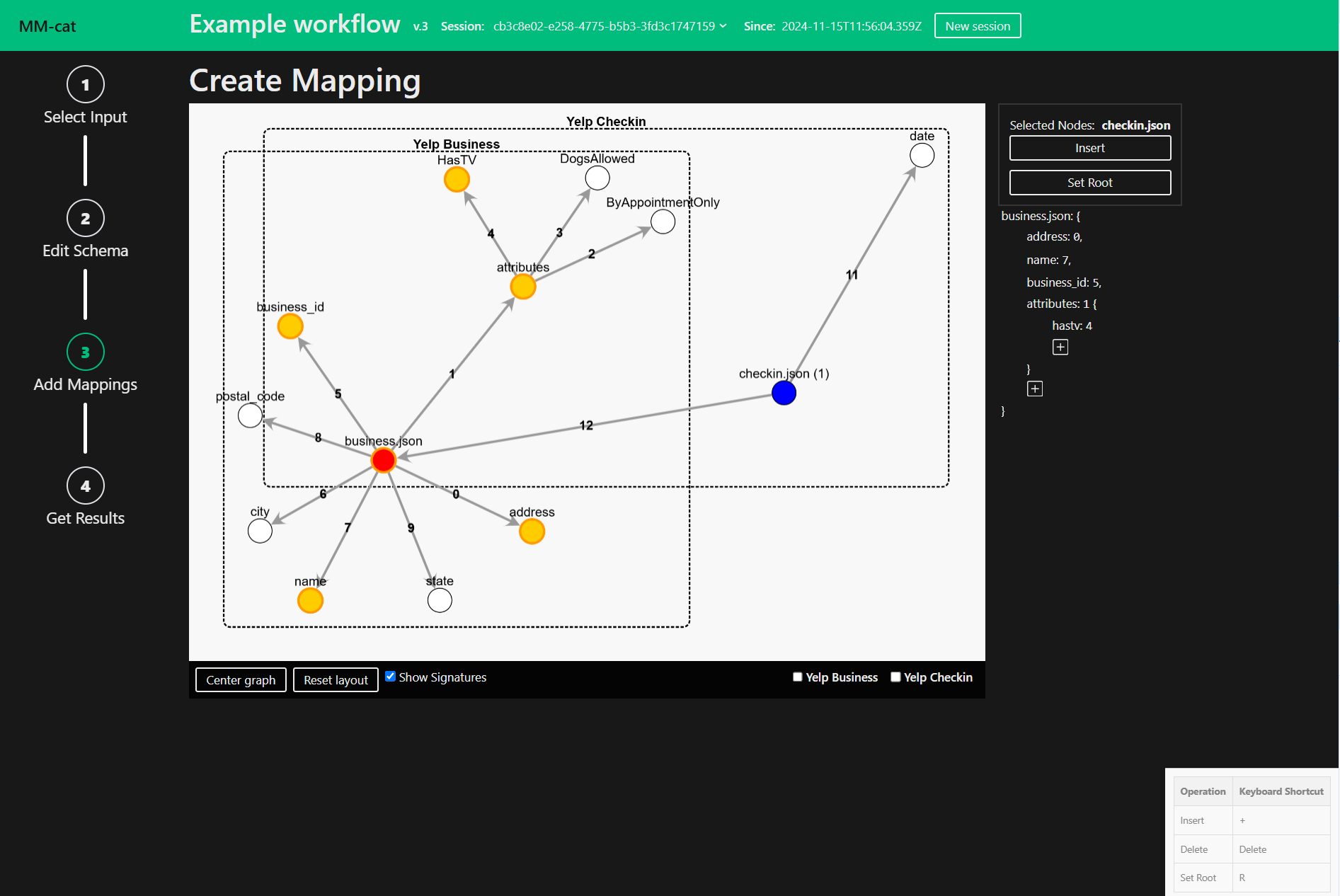
The Mapping Editor is a powerful tool in our application that enables users to create and manage mappings for multi-model data generation. This editor is an extension of an already existing mapping editor. Previously, users could add and edit properties by selecting nodes in the schema and manually adjusting them. The new Mapping Editor builds upon this foundation by introducing enhanced functionality and a streamlined workflow, offering a context menu as well as keyboard shortcuts for smooth and quick workflow.
See the Generation Workflow to learn more about the Mapping Editor.
-
Koupil, P., Hricko, S., & Holubová, I. Mm-infer: A tool for inference of multi-model schemas. (2022). https://doi.org/10.48786/EDBT.2022.52 ↩︎ ↩︎